Finding Your Feet with Peripheral Neuropathy
What is peripheral neuropathy?
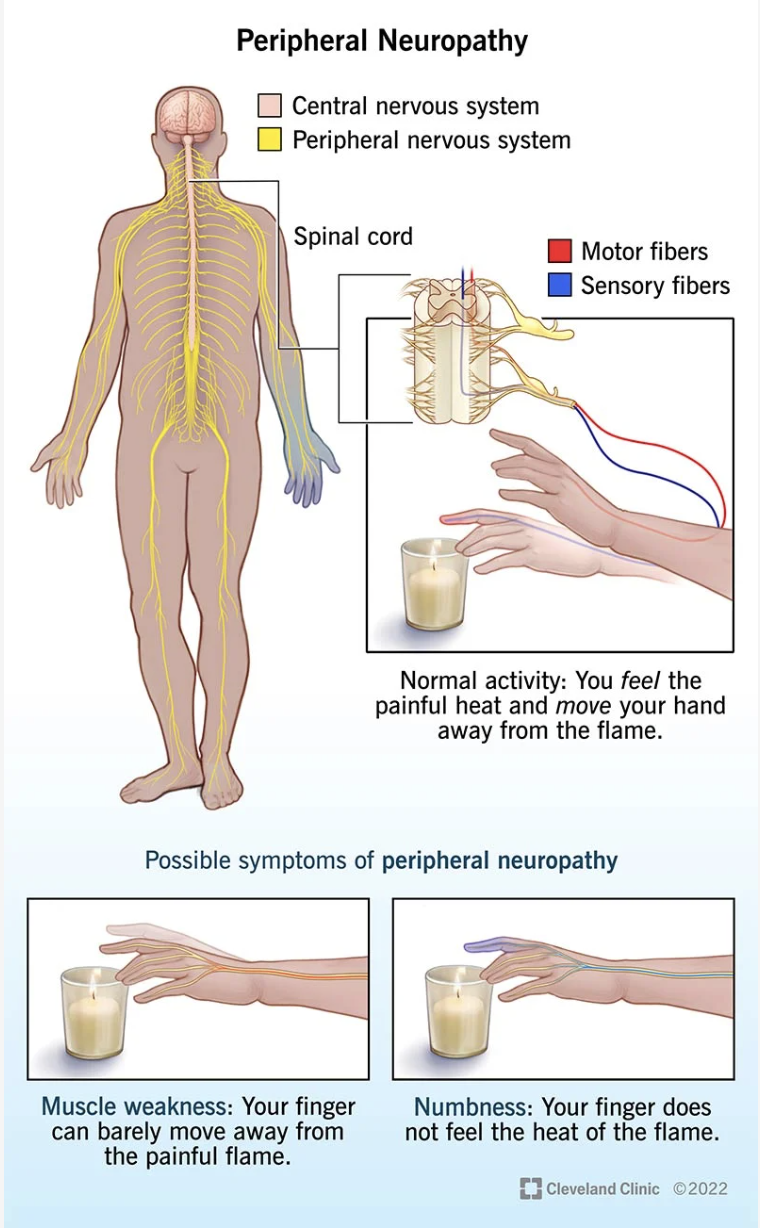
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is made up of the nerves that carry information to and from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Peripheral neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that affects the PNS. It is a relatively common condition, with estimates suggesting that it affects around 8% of the general population. It is more common in older adults, with the prevalence increasing with age.
Image source: Cleaveland Clinic https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-peripheral-neuropathy
There are a number of causes of peripheral neuropathy
Diabetes: Diabetes is a common cause of peripheral neuropathy, and it is estimated that around 60-70% of people with diabetes will develop the condition at some point. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves over time, leading to neuropathy.
Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol abuse can also lead to neuropathy, as alcohol can damage the nerves directly and also interfere with the body's ability to absorb essential nutrients such as B vitamins.
Medications: Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and certain antibiotics, can cause neuropathy as a side effect.
Trauma: Physical trauma to the nerves, such as from a fracture or surgery, can also cause neuropathy.
Genetic factors: Some people may be more prone to neuropathy due to inherited genetic factors.
Symptoms
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the type and severity of the nerve damage. Common symptoms include:
Numbness: This can feel like a dullness, or a complete lack of sensation in the affected area.
Tingling: This can feel like a tingling “pins and needles” or crawling sensation on the skin.
Burning: Some people with neuropathy may experience a burning sensation in the affected area.
Muscle weakness: Neuropathy can cause weakness in the arm and leg muscles, leading to difficulty with activities such as walking or gripping objects.
How is peripheral neuropathy managed?
There are a range of treatment options available for the management of peripheral neuropathy, including medications, lifestyle changes, and physiotherapy. Neurological physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option, where we focus on optimising sensation, strength, balance and mobility. Education is a vital part of your management - understanding how this condition is affecting your body allows us to target exercises directly at the affected areas, as well as honing in on unaffected systems to achieve the best function overall.
For example, if your sensation is the biggest problem, we might build up control and strength in your small foot muscles (that help make small adjustments on uneven ground and can also stimulate sensory input) as well as maximise function of the visual and inner ear balance systems so that your overall balance is as good as possible.
Other treatment areas include:
Strength training: We may recommend exercises to improve muscle strength, with weights or resistance band exercises. These can help to improve overall function and reduce the risk of falls.
Balance training: Balance training can help to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. This can be achieved through activities such as standing on one leg, or using balance boards or functional balance training.
Coordination training: Coordination exercises can help to improve the ability to move smoothly and efficiently. This can be achieved through activities such as catching and throwing a ball, or using hand-eye coordination games.
Endurance training: Endurance training can help to improve the ability to perform activities for longer periods of time, such as walking or carrying out household tasks. This can be achieved through activities such as walking or cycling, or through the use of cardio machines such as treadmills or stationary bikes.
Hydrotherapy: Aquatic physiotherapy can be very helpful in the management of pain or with patients who have high fear of falls in addition to all of the above.
Our team of highly trained physiotherapists works with clients to develop personalised treatment plans that are tailored to their specific needs and goals. We also have exercise physiology who can address the general health factors that contribute to peripheral neuropathy, such as diabetes and lack of physical activity.
References:
Mayo Clinic, Peripheral Neuropathy. Retrieved January 6, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061
NINDS Peripheral Neuropathy Fact Sheet. National Institute of Health. Retrieved January 6, 2023, from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/peripheral-neuropathy-fact-sheet"
Cleveland Clinic Peripheral Neuropathy. My.Clevelandclinic.org. Retrieved January 6, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-peripheral-neuropathy
Streckmann, F., Zopf, E.M., Lehmann, H.C. et al. Exercise Intervention Studies in Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Sports Med 44, 1289–1304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0207-5